CXCL5 drives obesity to diabetes, and further.
Résumé
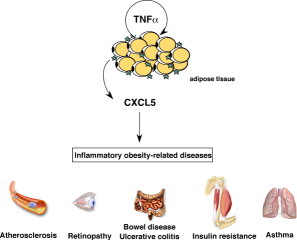
We have recently shown that the CXCL5 chemokine is secreted by adipose tissue in the obese state. We demonstrated that adipose tissue-derived CXCL5 mediates insulin resistance in muscle. We speculate in this paper that CXCL5 could also mediate other obesity, and diabetes-derived pathologies, such as cardiovascular disease, retinopathy, or inflammatory bowel disease. In this scenario CXCL5 targeted therapy would prevent not only the development of type II diabetes in obese subjects, but also several other obesity-related co morbidities. Finally we propose to analyze the CXCL5 gene to find particular polymorphisms that could predict the development of type II diabetes in obese subjects.
Domaines
Endocrinologie et métabolisme
Fichier principal
 schema.pdf (1.78 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
edited-CXCL5-aging-3.pdf (400.44 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
schema.pdf (1.78 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
edited-CXCL5-aging-3.pdf (400.44 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Origine : Fichiers produits par l'(les) auteur(s)
Origine : Fichiers produits par l'(les) auteur(s)