High plasma leptin predicts an increase in subcutaneous adiposity in children and adults.
Résumé
Objective:To investigate the hypothesis that plasma leptin may predict adiposity changes.Design:A population-based cohort study.Setting:Fleurbaix and Laventie, in the north of France.Subjects:In all, 1175 subjects participated, of whom 946 completed measurements at baseline (1999) and follow-up (2001). After excluding 64 subjects obese at baseline, 882 subjects (478 adults, 404 children 8 years and over) were included in the analysis.Interventions:We measured plasma leptin concentrations at baseline and various adiposity parameters at baseline and follow-up. Partial correlation coefficients (r (p)) between baseline plasma leptin and each adiposity indicator at follow-up were calculated with adjustment for baseline age, pubertal stage, adiposity and familial correlations between siblings.Results:Changes in body mass index and percentage body fat were not related to baseline plasma leptin. High baseline plasma leptin predicted an increase (r (p) (P-value)) in the sum of the four skinfolds (0.18 (<0.0001)), the waist circumference (0.16 (0.0003)) and the waist-to-hip ratio (0.29 (<0.0001)) in adults only, and in the hip circumference in adults (0.20 (<0.0001)) and children (0.22 (<0.0001)). After adjustment for a set of four adiposity variables at baseline (percentage body fat, skinfolds, waist and hip circumferences), baseline plasma leptin predicted only changes in the sum of the four skinfolds in adults (0.15 (0.001)), with similar tendency although not significant in children (0.08 (0.13)).Conclusions:A high leptin relative to baseline fat mass predicts fat mass gain over time, mainly in the subcutaneous location.Sponsorship:Supported by Knoll, Centre d'Etudes et de Documentation du Sucre (CEDUS), Groupe Fournier, Lesieur, Nestl?rance, Produits Roche, Le Centre d'Information Scientifique sur la Bi? (CISB).European Journal of Clinical Nutrition advance online publication, 13 December 2006; doi:10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602579.
Domaines
Santé publique et épidémiologie
Fichier principal
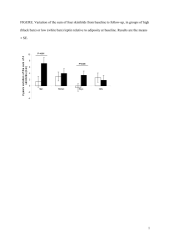 FigureArticleLeptine.pdf (64.46 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Table_11.pdf (67.72 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Table_21.pdf (68.32 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Table_31.pdf (66.08 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Table_41.pdf (72.12 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
leptine_EJCN.pdf (230.25 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
FigureArticleLeptine.pdf (64.46 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Table_11.pdf (67.72 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Table_21.pdf (68.32 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Table_31.pdf (66.08 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Table_41.pdf (72.12 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
leptine_EJCN.pdf (230.25 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier